Diverticulitis: What Is it and How to Treat it
Diverticulitis is a condition in which small pouches or sacs called diverticula form in the large intestine, or colon, and become inflamed. When the sacs are inflamed, they can bulge outward and cause abdominal pain and discomfort. In addition to abdominal pain, several other symptoms can be associated with diverticulitis. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms associated with this condition, see a gastroenterologist for a diagnosis and possible treatment options.

Symptoms & Causes
The exact cause of diverticulitis is unclear. However, there seems to be a link between a diet too low in fiber and the development of diverticulitis. When fiber is lacking in the diet, the colon works harder to move stools through the intestinal tract. It is possible that the pressure from the increased effort to move the stool can lead to the formation of diverticula along with the interior of the colon or large intestine. Maintaining a diet with sufficient fiber intake can potentially help prevent diverticulitis.
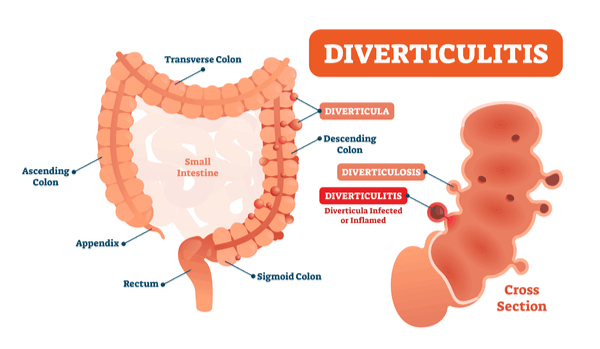
Various symptoms can be associated with diverticulitis. Abdominal pain is a common symptom and tends to be felt primarily on the left side. Other symptoms associated with diverticulitis include:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- chills
- abdominal pain
- cramping
- constipation
- bloating
Treatment
A variety of options are available for treating diverticulitis. For less severe cases, a combination of antibiotics, pain relievers and a liquid diet can be sufficient to resolve the diverticulitis. More serious cases of diverticulitis in which patients cannot drink liquids can require a hospital stay. While in the hospital, all nutrition will be obtained intravenously. Avoiding eating and drinking by mouth gives the bowel time to rest and recover and can help clear up the diverticulitis. If the condition is still severe, surgery might be required.
Diverticulitis can result in a lot of pain and discomfort. Fortunately, there are treatments that can provide relief. See a gastroenterologist for diagnosis and a treatment plan.