Most medications can be continued as usual, but some medications can interfere with the preparation or the examination. Inform your doctor about medications you’re taking, particularly aspirin products, arthritis medications, anticoagulants (blood thinners such as warfarin or heparin), clopidogrel, insulin or iron products. Also, be sure to mention allergies you have to medications.
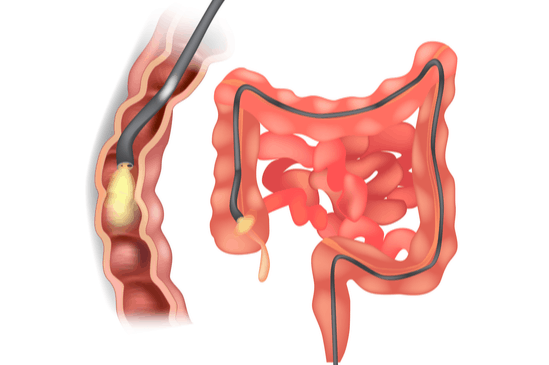
Colonoscopy is well-tolerated and rarely causes much pain. You might feel pressure, bloating or cramping during the procedure. Typically, your doctor will give you a sedative or painkiller to help you relax and better tolerate any discomfort. You will lie on your side or back while your doctor slowly advances a colonoscope along your large intestine to examine the lining. Your doctor will examine the lining again as he or she slowly withdraws the colonoscope. The procedure itself usually takes less than 45 minutes, although you should plan on two to three hours for waiting, preparation and recovery. In some cases, the doctor cannot pass the colonoscope through the entire colon to where it meets the small intestine. Your doctor will advise you whether any additional testing is necessary.
If your doctor thinks an area needs further evaluation, he or she might pass an instrument through the colonoscope to obtain a biopsy (a small sample of the colon lining) to be analyzed. Biopsies are used to identify many conditions, and your doctor will often take a biopsy even if he or she doesn’t suspect cancer. If colonoscopy is being performed to identify sites of bleeding, your doctor might control the bleeding through the colonoscope by injecting medications or by cauterization (sealing off bleeding vessels with heat treatment) or by use of small clips. Your doctor might also find polyps during colonoscopy, and he or she will most likely remove them during the examination. These procedures don’t usually cause any pain.
Polyps are abnormal growths in the colon lining that are usually benign (noncancerous). They vary in size from a tiny dot to several inches. Your doctor can’t always tell a benign polyp from a malignant (cancerous) polyp by its outer appearance, so he or she will usually remove polyps for analysis. Because cancer begins in polyps, removing them is an important means of preventing colorectal cancer.
Colonoscopy and polypectomy are generally safe when performed by doctors who have been specially trained and are experienced in these procedures. One possible complication is a perforation, or tear, through the bowel wall that could require surgery. Bleeding might occur at the site of biopsy or polypectomy, but it’s usually minor. Bleeding can stop on its own or be controlled through the colonoscope; it rarely requires follow-up treatment. Some patients might have a reaction to the sedatives or complications from heart or lung disease. Although complications after colonoscopy are uncommon, it’s important to recognize early signs of possible complications. Contact your doctor if you notice severe abdominal pain, fever and chills, or rectal bleeding. Note that bleeding can occur several days after the procedure.