Colon Cancer Screening
One of the most effective screening methods for detecting the earliest signs of colorectal cancer is through a colonoscopy. A colonoscopy allows a gastroenterologist to be able to examine the lining of the rectum and colon (lower intestines) to look for precancerous polyps and other warning signs. These precancerous polyps can also be removed during a colonoscopy before they have the chance to develop into cancer. This is why colon cancer screenings are so important.
Who should get regular colon cancer screenings?
Men and women who are between the ages of 45 and 75 should see their gastroenterologist for regular colon cancer screenings. While there are other methods for screening for colon cancer (e.g. stool test; flexible sigmoidoscopy) a colonoscopy is the most effective and accurate screening tool available.
If a patient has never had polyps or other precancerous warning signs they may not need to get further colorectal cancer screenings after age 75. Patients with risk factors may require additional routine screenings after the age of 75.
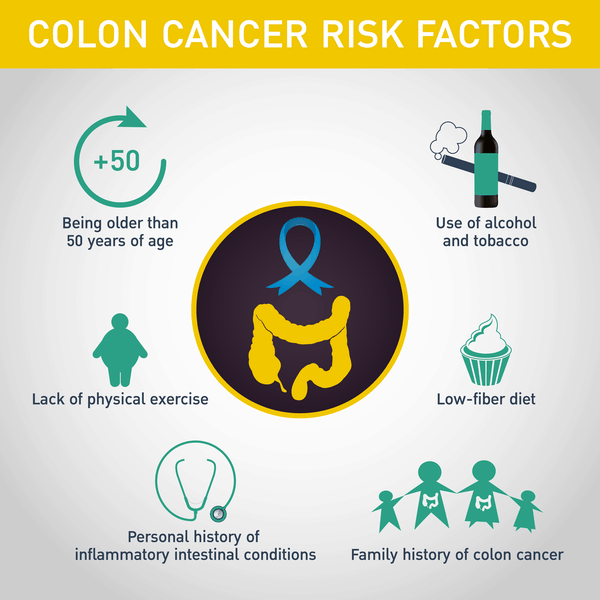
Of course, sometimes it’s necessary to get a colon cancer screening before 45 years old. You may benefit from getting tested earlier if:
- You or an immediate family member has a history of colorectal polyps or colon cancer
- You’ve been diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. Crohn’s disease; ulcerative colitis)
- You lead an inactive, sedentary lifestyle
- You have a poor diet that is high in fat and low in fiber
- You’ve been diagnosed with diabetes
- You are obese
- You are a heavy alcohol consumer
- You are a smoker
- You’ve undergone radiation therapy to treat cancer
If you have any risk factors it’s important that you talk with your gastroenterologist to find out when you should start getting regular screenings and which screening is right for you based on your health coverage.
What should I expect from a colorectal cancer screening?
As we mentioned, the most common screening tool for colon cancer is a colonoscopy. During this procedure, we will insert a thin flexible tube (called an endoscope) into the rectum and gently guide it through the large intestines. At the end of this endoscope is a camera. This camera will allow your GI doctor to look for polyps and other problem. If polyps are found they can be removed during your colonoscopy. If nothing is found during your diagnostic testing, a colonoscopy can take as little as 30 minutes. The patient will be under the effects of conscious sedation throughout the procedure.
Do you have questions about getting a colonoscopy? Is it time to schedule your first routine colon cancer screening? If so, then call your intestinal doctor today.